Here's a summary of the news about the magnetically-steerable micro-robot for kidney stones: ## Micro-Robot Offers New Hope for Kidney Stone Treatment **News Title:** Wiggling magnetic micro-robot goes after kidney stones **Report Provider:** New Atlas **Author:** Tsester/CC 1.0 **Publication Date:** August 13, 2025 ### Overview A groundbreaking development from the University of Waterloo in Canada offers a potential new solution for individuals suffering from recurring and difficult-to-treat kidney stones. Researchers, led by Dr. Veronika Magdanz, have developed a tiny, magnetically-steerable micro-robot designed to dissolve kidney stones directly at their location within the urinary tract. This innovation aims to provide a more effective and less invasive alternative to current treatments, which often involve oral medications with slow action or surgical interventions. ### Key Findings and Technology * **The Micro-Robot:** The device is a **1 x 1 x 12-mm filament** made from a hydrogel/elastomer blend. It is loaded with the enzyme **urease** and contains a **micro-magnet** at one end. * **Mechanism of Action:** * The filament is inserted into the bladder via a catheter. * It is then guided to the kidney stone using external imaging (ultrasound) and an external robotic arm equipped with a rotating magnet. * The rotating magnet causes the filament to "wiggle" and navigate the urinary tract by pushing against its internal walls. * Once at the stone, the filament is held in place for several days using an external magnetic patch adhered to the skin. * The released urease enzyme increases the urine's pH, causing the kidney stone to dissolve. * **Dissolution Efficacy:** In tests conducted in a 3D-printed model of a human urinary tract with synthetic urine, the micro-robot demonstrated significant stone dissolution: * The pH of the urine was increased from a typical kidney stone environment of **6 to 7**. * Kidney stones **decreased in weight by an average of 30% over a five-day period**. This reduction is significant enough to allow for easier passage of the stones. * **Longevity of Effect:** The increase in urine pH, crucial for stone dissolution, was found to last for **up to three months**. * **Passage:** The filament itself is designed to be passed from the body in the same manner as dissolved stone fragments. ### Significance and Goals The primary goal of this research, as stated by lead scientist Dr. Veronika Magdanz, is to "provide an effective alternative to existing treatment methods." The team hopes that this accelerated stone dissolution will lead to faster pain relief and quicker stone passage for patients. ### Future Plans Studies on **large animals are now being planned** to further evaluate the safety and efficacy of this micro-robot technology. ### Publication The research detailing this innovation was recently published in the journal **Advanced Healthcare Materials**.
Wiggling magnetic micro-robot goes after kidney stones
Read original at New Atlas →Recurring kidney stones can be an agonizing, debilitating problem, particularly if they can't be treated by orally-administered medication. There may be new hope on the horizon, however, in the form of a tiny magnetically-steerable stone-dissolving "robot."Basically solid deposits of salt and other urine-related minerals, kidney stones aren't pleasant for anyone, as they can be very painful to pass through the urethra.
It's even worse for some people, though, in whose kidneys the stones regularly reoccur. Oral medications may or may not help dissolve the deposits, but even if they do work, they often take too long to do so. In cases where the stones are actually blocking the urinary tract, surgery is sometimes the only option.
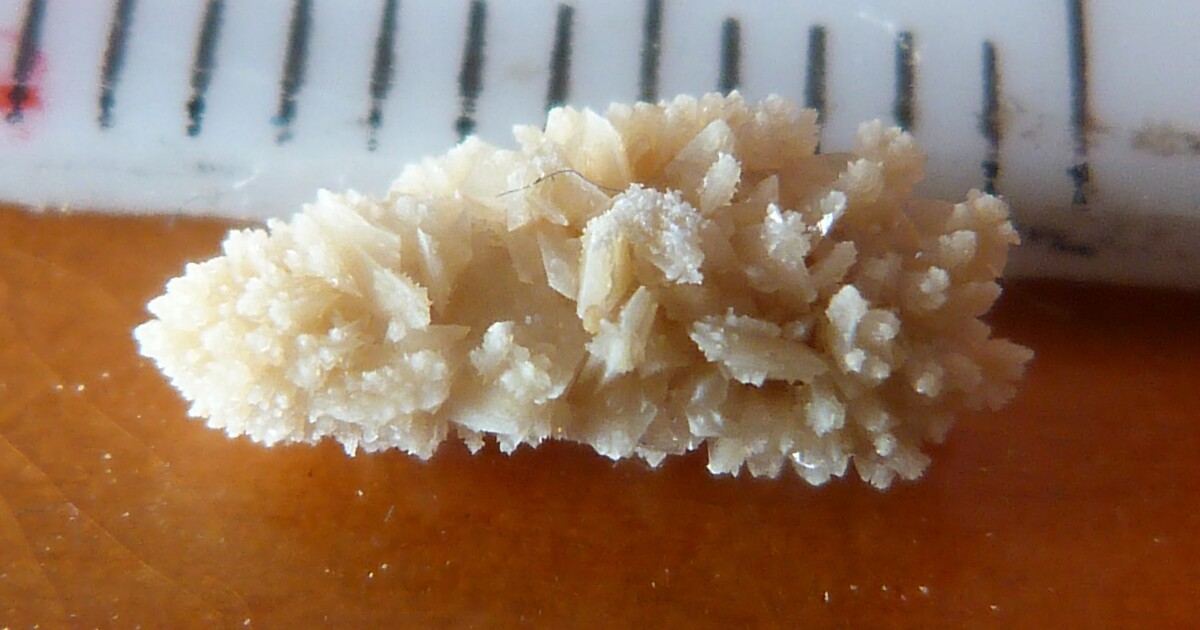
It would be much better if the medication could be delivered straight to the kidney stones, instead of being dispersed throughout the digestive system and bloodstream. That's where the soft-bodied "robot strip" comes in."She may not look like much, but she's got it where it counts" – one of the prototype stone-snuffing filaments University of WaterlooDeveloped by Dr.
Veronika Magdanz and colleagues at Canada's University of Waterloo, it presently takes the form of a 1 x 1 x 12-mm filament made of a hydrogel/elastomer blend that is loaded with an enzyme known as urease, and which contains a micro-magnet at one end. The idea is that the device could be inserted into the bladder via a catheter.
Once in the body, the filament can be imaged via ultrasound, and moved by an external robotic arm equipped with a rotating magnet at the end. As that magnet rotates, the filament likewise wiggles back and forth, making its way through the urinary tract by pushing off against its inner walls.Upon reaching the kidney stone, the filament is stopped.
It can then be held in place for several days via an external magnetic patch that's adhered to the skin.As the filament sits, it releases its urease into the surrounding urine, increasing the liquid's pH. That decrease in acidity causes the stone to dissolve, until it can be passed with the urine relatively painlessly.
The filament can ultimately be passed in the same manner.Lead scientist Dr. Veronika Magdanz (left) and team member Afarin Khabbazian, along with the arm used to guide the filamentsUniversity of WaterlooIn tests performed in a 3D-printed model of a human urinary tract filled with synthetic urine, one of the filaments was found to increase the pH of the liquid from 6 – typical of a kidney stone environment – up to 7.
This caused kidney stones in the urine to decrease in weight by an average of 30% over a five-day period, which would allow them to be easily passed.What's more, the increase in pH lasted for up to three months. Studies on large animals are now being planned."Our goal is to provide an effective alternative to existing treatment methods," says Magdanz.
"We hope accelerated stone dissolution will relieve the pain faster and help patients pass stones quicker."A paper on the research was recently published in the journal Advanced Healthcare Materials.Source: University of Waterloo